| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
When you install the Intelligent Agent on Windows NT, a service called OracleAgent (or OracleAgent80) is created. To start the Intelligent Agent, open the Control Panel folder and select the Services icon. Scroll down until you find OracleAgent, highlight it, and press the Start button. When the Agent is started for the first time, it will use the Windows NT Registry, your listener.ora file, and the tnsnames.ora file to create the configuration files snmp_ro.ora, snmp_rw.ora, and services.ora. You can also start, stop, and obtain the status of the Agent from a DOS prompt by typing net start oracleagent and net stop oracleagent, respectively. Simply typing net start enables you to see whether the Agent is already running.
Warning:
If you are automating the startup and shutdown of the Intelligent Agent on a UNIX platform, be careful. Under some circumstances, the Agent might not shut down properly, and the dbsnmp process that is left can use large amounts of your system’s CPU. It is a good idea to follow up the lsnrctl dbsnmp_stop command in your script with a series of commands to list processes, grep for dbsnmp, and kill any remaining dbsnmp processes.
Discovering New Services
The last step you must perform before you can fully utilize Enterprise Manager is to discover new services on the servers you’d like to monitor. Service Discovery defines the services in the Repository and adds them to your tnsnames.ora file so you can monitor the databases and listeners, schedule jobs, and perform administrative tasks from the OEM console.
Select the Enterprise Manager icon from the Oracle Enterprise Manager program group. On the sign-on screen, enter the ID and password for the Repository owner and the connect string for the Repository database.
When the OEM console appears, select the Service Discovery option from the Navigator menu. The Discover New Services Wizard will ask whether you would like to proceed with service discovery. Click on the Next button to leave the introduction window and proceed with service discovery.
On the next screen, enter the name of each node on which you have configured an Intelligent Agent, pressing the Add button after each entry.
On the Discovery Interval screen, shown in Figure 21.2, it is best to take the default and allow the wizard to update your tnsnames.ora file. If you want to automatically discover new services throughout the day, enter the interval at which you would like this discovery to take place.

Figure 21.2. The Discovery Interval window.
One final window will appear before the discovery begins. This window simply summarizes your choices and shows you any previously discovered nodes that will be refreshed.
If a node is accessible and the server’s Intelligent Agent is contacted, you should receive a status of Discovered in the Service Discovery Status window.
You can now use the Navigator to see the databases and listeners you’ve discovered. If you double-click on one of the databases, you will be warned that no preferences are set for that database, and a sign-on screen will appear.
Setting Preferences
Before you can schedule jobs, you need to set user preferences for that database. This will also enable you to connect to the database from the Navigator window without entering a user ID and password.
The Job Scheduling system and the Navigator will use the username and password defined in user preferences to run an operating system job or connect to a database. You can open the User Preferences window by selecting Preferences from the File menu. On the User Preferences window, select each service and provide the username and password you would like to use for each service (see Figure 21.3). Notice to the left of the User Preferences window that the services discovered in the previous section are now accessible through the Navigator system.
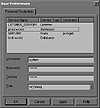
Figure 21.3. Setting the preferred credentials.
Managing Events
An event in Enterprise Manager is anything that might occur on the database server or in the database, which Enterprise Manager is capable of monitoring. Events are grouped into event sets or a collection of related events. You tell Enterprise Manager to monitor for an event set by registering the event set for a specific node or database. You also define which administrator or operator should be notified if an event within the set occurs and the method of that notification: email, pager, or a message to the OEM Console.
Keep in mind that each Repository is assigned to a specific administrator. If an administrator is monitoring a database for one event and a second administrator is monitoring the same database for a second event, each administrator will receive notification of only his or her own events, not the events of the other administrator. The Intelligent Agent routes the messages according to the owner of the Repository in which the event is registered. This is why you should not create multiple repositories owned by the same user ID.
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |